Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

In the intricate and evolving landscape of Greenlandic governance, the role of the Prime Minister, often referred to as the “PM” or the “Premier of Greenland. “occupies a pivotal and influential position. As an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, Greenland’s political framework is uniquely tailored to accommodate a degree of self-governance while maintaining ties with Denmark. Understanding the Premier of Greenland’s role within this context is essential for grasping the nuances of Greenland’s political dynamics and its interactions on the global stage. The current incumbent is Jens-Frederik Nielsen.
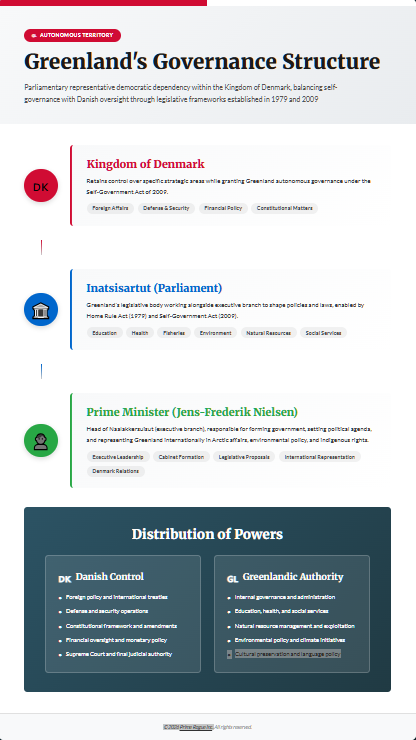
Greenland’s political structure is a fascinating tapestry woven with threads of autonomy and dependency, shaped by historical and contemporary legislative frameworks. Its governance model reflects a blend of Greenlandic self-determination and Danish oversight, creating a system that requires careful navigation by its leaders.
Greenland operates within a parliamentary representative democratic dependency, a status that emerged from historical legislative acts. The Home Rule Act of 1979 marked a significant turning point, granting Greenland greater control over its internal affairs. This was further enhanced by the Self-Government Act of 2009, which expanded Greenland’s autonomy and allowed it to assume responsibility for areas such as education, health, and fisheries.
Despite this autonomy, Greenland remains part of the Kingdom of Denmark, and certain areas, including foreign affairs, security, and financial policy, remain under Danish control. This complex relationship demands a leadership that can adeptly manage both domestic governance and international relations, ensuring that Greenland’s voice is heard while maintaining a harmonious relationship with Denmark.
The legislative framework governing Greenland is designed to balance self-governance with the overarching authority of Denmark. The Inatsisartut, Greenland’s Parliament, plays a critical role in this structure, working alongside the executive branch to shape policies and laws. The distribution of power requires a nuanced understanding of both legislative processes and the political landscape, enabling the Prime Minister to effectively navigate this system.
The Home Rule Act and the Self-Government Act provide the legal basis for Greenland’s autonomy, delineating the powers and responsibilities of Greenlandic authorities. These acts have been instrumental in shaping Greenland’s political identity, allowing it to assert its interests while remaining part of the Danish realm.
The relationship between Greenland and Denmark is characterized by both cooperation and negotiation. Denmark retains control over areas such as defense and foreign policy, necessitating ongoing dialogue between Greenlandic and Danish authorities. This interaction is crucial for ensuring that Greenland’s interests are represented at the international level and that the unique challenges facing the territory are addressed in a manner that respects its autonomy. This has become especially salient since the beginning of President Donald Trump’s threats to annex Greenland largely resulting from the strategic importance of Greenland relative to the GIUK Gap and Greenland’s mineral reserves.
The Prime Minister of Greenland plays a key role in these interactions, working to maintain a productive relationship with Denmark while advocating for Greenland’s interests. This requires diplomatic skill and a deep understanding of both domestic and international politics, enabling the Prime Minister to effectively represent Greenland on the global stage.
The Prime Minister of Greenland, known as the Premier, currently Jens-Frederik Nielsen, is the head of the Naalakkersuisut, which serves as the executive branch of Greenland’s government. This role encompasses a wide range of responsibilities, from forming a government to representing Greenland internationally, and requires a leader who can effectively balance these diverse duties.
As the head of the Naalakkersuisut, the Prime Ministeris responsible for forming a government, which involves appointing ministers to oversee various departments. This executive body is tasked with implementing policies and managing the day-to-day affairs of the territory, ensuring that government functions operate smoothly and effectively.
The Prime Minister of Greenland sets the political agenda, guiding the direction of Greenlandic governance and prioritizing issues that are critical to the territory’s development. This involves making strategic decisions, coordinating with other government officials, and ensuring that policies align with the needs and aspirations of the Greenlandic people.
While the Prime Minister of Greenland holds significant executive power, collaboration with the Inatsisartut is essential for effective governance. The Prime Minister plays an instrumental role in proposing legislation and must engage in negotiations with parliamentary members to secure the passage of laws. This requires a deep understanding of parliamentary procedures, political negotiation skills, and the ability to build consensus among diverse political factions.
The Prime Minister of Greenland must also navigate the complexities of a multi-party system, working with various political groups to achieve common goals. This collaboration is vital for ensuring that legislation reflects the needs and priorities of the Greenlandic population, fostering a democratic and inclusive political environment.
Although Denmark handles foreign policy, the Prime Minister of Greenland plays a crucial role in representing the territory in international forums. This is particularly important in areas such as Arctic affairs, environmental policy, and indigenous rights, where Greenland has unique interests and concerns. This role continues to grow significantly because of American threats to Greenland, and the growing importance of Arctic sovereignty.
The Prime Minister of Greenland often participates in international conferences and bilateral meetings, sometimes alongside the Prime Minister of Denmark, advocating for Greenland’s interests and forging partnerships that benefit the territory. This requires diplomatic acumen and a comprehensive understanding of global issues, enabling the Prime Minister to effectively represent Greenland on the world stage and contribute to international discussions. Greenlandic allies like Canada, notably because of CFS Alert being close to Greenland, are critical partners for the Prime Minister of Greenland.
The Prime Minister of Greenland faces a range of challenges that require strategic thinking and effective leadership. These challenges span from balancing autonomy with dependence to addressing economic and environmental issues that are crucial to Greenland’s future.
One of the primary challenges faced by the Prime Minister is balancing Greenland’s autonomy with its dependence on Denmark. This involves negotiating the terms of self-governance and ensuring that Greenland’s voice is heard in matters still under Danish control. The Premier of Greenland must carefully navigate this relationship, advocating for Greenland’s interests while maintaining a positive and collaborative partnership with Denmark.
This balancing act requires diplomatic skill and a deep understanding of both Greenlandic and Danish political landscapes. The Prime Minister must work to enhance Greenland’s autonomy while recognizing the benefits of its association with Denmark, ensuring that both parties’ interests are respected and addressed.
Greenland’s economy is heavily reliant on fishing and hunting, with emerging interests in tourism and natural resource exploration. The Prime Minister of Greenland must navigate the complexities of promoting economic development while preserving the unique cultural and environmental heritage of Greenland. This involves developing policies that support economic growth, attract investment, and create jobs, while ensuring that these initiatives are sustainable and environmentally responsible. Tourism, like vacations in Greenland, also represents a growing axis of Greenlandic economic growth.
The Premier of Greenland must also address the impacts of climate change, which are particularly pronounced in the Arctic region. This requires collaboration with international bodies and the implementation of sustainable practices that align with global environmental standards, ensuring that Greenland’s economy can thrive in a rapidly changing world.

Greenland is at the forefront of climate change discussions due to its rapidly melting ice sheets. The Prime Minister of Greenland must address the environmental challenges posed by climate change, which have significant implications for Greenland’s economy, infrastructure, and way of life. This requires a comprehensive approach to environmental policy, balancing the need for economic development with the imperative to protect Greenland’s fragile ecosystems.
The Prime Minister must work with international partners to address climate change, advocating for policies that reduce emissions and promote sustainability. This involves participating in global discussions, forging partnerships with other countries, and implementing practices that protect Greenland’s environment for future generations including the facilitation of arctic and polar research.
As Greenland looks to the future, the role of the Prime Minister will be crucial in shaping the territory’s path toward greater autonomy and self-determination. This involves navigating complex political, economic, and social issues, and ensuring that Greenland’s governance structures are robust and effective.
There has been ongoing debate within Greenland regarding the pursuit of full independence from Denmark. The Prime Minister plays a crucial role in this discourse, weighing the economic, social, and political implications of such a move. While independence remains a long-term aspiration for some, the Premier of Greenland must ensure that any steps toward this goal are carefully considered and strategically executed.
The pursuit of independence involves assessing the potential benefits and challenges, from economic viability to international recognition. The Premier of Greenland must engage with Greenlandic citizens, political leaders, and international partners to develop a clear vision for the territory’s future, ensuring that any move toward independence is grounded in careful planning and strategic foresight.
The Prime Minister of Greenland is also tasked with strengthening Greenland’s democratic institutions to ensure transparency, accountability, and effective governance. This involves promoting civic engagement, enhancing the capacity of governmental bodies, and safeguarding the rights of the Greenlandic people. Strengthening these institutions is crucial for building a resilient and responsive political system that can address the challenges of the future.
The Prime Minister of Greenland must also work to foster a culture of democracy and participation, encouraging citizens to engage in political processes and contribute to the development of their communities. This involves supporting initiatives that promote education, awareness, and involvement, ensuring that Greenland’s democratic institutions are robust and inclusive.
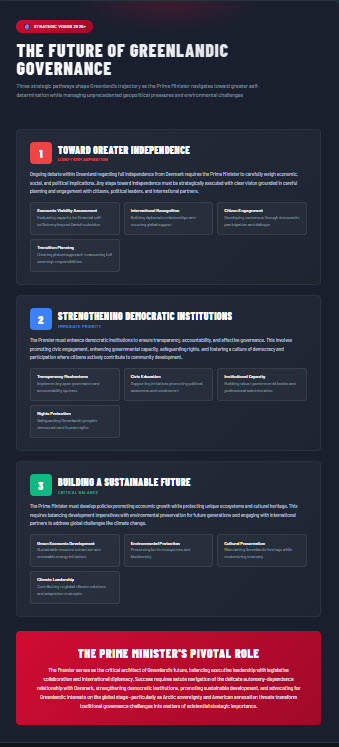
The future of Greenlandic governance also involves addressing the challenges of sustainability and environmental responsibility. The Premier must work to develop policies that promote economic growth while protecting Greenland’s unique ecosystems and cultural heritage. This involves balancing the need for development with the imperative to preserve Greenland’s environment for future generations.
The Prime Minister of Greenland must also engage with international partners to address global challenges such as climate change, ensuring that Greenland is part of the solution. This requires a commitment to sustainable practices and collaboration with other countries, enabling Greenland to contribute to global efforts to combat climate change and protect the planet.
The role of Greenland’s Premier is multifaceted, encompassing executive leadership, legislative interaction, and international representation. As Greenland navigates the complexities of its unique political status, the Premier of Greenland serves as a pivotal figure in shaping the territory’s future. By addressing the challenges of economic development, environmental sustainability, and potential independence, the Greenlandic Prime Minister plays a critical role in ensuring the prosperity and well-being of its people.
The delicate balance of autonomy and dependence on Denmark requires astute leadership and a strategic vision for the future of Greenlandic governance. The Prime Minister must work to strengthen democratic institutions, promote sustainable development, and advocate for Greenland’s interests on the international stage, ensuring that the territory can thrive in an increasingly interconnected and challenging world. The role of the Greenlandic Prime Minister will only continue to grow as arctic sovereignty and Nordic security continue to emerge as critical variables.