Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM

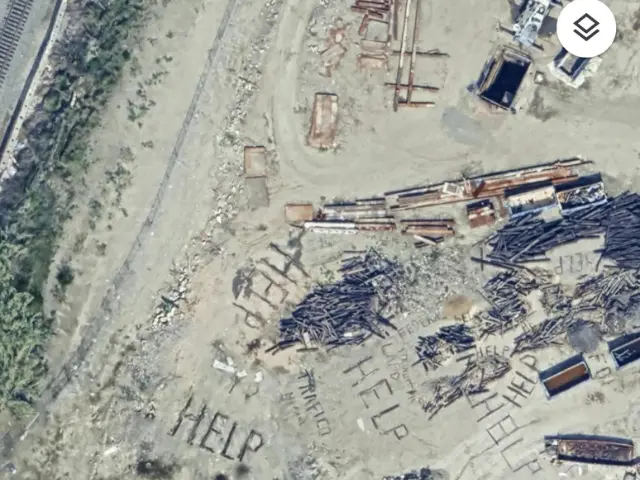
Los Angeles, a bustling metropolis known for its entertainment industry and diverse culture, harbors a dark reality—an entrenched human trafficking crisis. As one of the largest hubs for trafficking in the United States, the city’s extensive transportation networks, proximity to international borders, and economic disparities make it a prime target for traffickers looking to exploit vulnerable individuals. Victims are often coerced into forced labor, sexual exploitation, and domestic servitude, hidden in plain sight across the city’s sprawling urban landscape. Recent signs mentioning trafficking and asking for help near Los Angeles’ Union Pacific railroad yard are leading to growing worry about human trafficking in Los Angeles.
Despite efforts from law enforcement and advocacy groups, human trafficking in Los Angeles continues to thrive, adapting to new challenges posed by digital technology and economic instability. This article explores the current state of human trafficking in LA, including alarming statistics, key trafficking corridors, the role of law enforcement, and what is being done to combat this pervasive issue.
Los Angeles is often labeled as a trafficking epicenter due to its unique combination of factors that create a fertile ground for exploitation. The city’s vast network of highways, its bustling international port, and its large undocumented population make it a primary transit point for traffickers looking to move victims both domestically and internationally. The California Department of Justice reports that nearly 60% of trafficking cases in the state are concentrated in the greater Los Angeles area, with a growing number of victims being minors.
The underground nature of human trafficking means that official numbers often represent only a fraction of the actual scale. According to advocacy organizations, for every reported trafficking case, there are potentially ten or more victims who remain invisible, trapped in the cycle of abuse. Women and children make up the majority of trafficking victims, but a rising trend of male labor trafficking cases has also been noted in industries such as agriculture, construction, and hospitality.
The financial incentives for traffickers are staggering. The International Labour Organization (ILO) estimates that human trafficking generates over $150 billion annually worldwide, with Los Angeles contributing a significant portion due to its strategic location and high demand for cheap labor and illicit services. Traffickers leverage technology to their advantage, using encrypted communication apps, online classified ads, and social media to recruit and control victims.
Despite widespread efforts by law enforcement to crack down on trafficking networks, the deeply embedded infrastructure that supports exploitation—ranging from fraudulent employment agencies to corrupt business practices—makes it difficult to eradicate. The lucrative nature of the industry ensures that traffickers are willing to adapt, continuously evolving their tactics to evade detection.
Traffickers in Los Angeles operate through a variety of deceptive tactics designed to lure individuals into exploitative situations while avoiding suspicion from authorities. The most commonly observed methods include false job offers, romantic manipulation, and coercion through debt bondage. Traffickers often advertise seemingly legitimate jobs in industries such as hospitality, caregiving, and entertainment, promising high wages and good working conditions. Once victims arrive, their documents are confiscated, and they are subjected to physical and psychological abuse to ensure compliance.
Social media platforms have become a dominant recruitment tool, with traffickers using apps like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat to identify vulnerable individuals. Victims are often groomed over weeks or months, with traffickers building trust before coercing them into exploitative situations. Online grooming, where traffickers pose as potential employers, romantic partners, or mentors, has become a leading entry point into trafficking networks.
Debt bondage remains a critical issue in labor trafficking cases across Los Angeles. Victims, primarily from Latin America and Asia, are often promised a pathway to citizenship or stable employment but are instead trapped in exploitative working conditions, forced to “pay off” exorbitant fees for their transportation, housing, and basic necessities. Many are kept in isolated environments, making it difficult for them to seek help or escape.
Traffickers also use fear-based tactics, threatening to report undocumented workers to immigration authorities if they resist. This fear, combined with language barriers and social isolation, creates a powerful deterrent that keeps victims compliant. In neighborhoods such as Koreatown, Chinatown, and Little Central America, traffickers take advantage of tight-knit communities to maintain control, relying on cultural and linguistic isolation to prevent victims from reaching out to law enforcement. Natural disasters like the ongoing California wildfires also increase human trafficking vulnerability.
Several areas in Los Angeles have been identified as trafficking hotspots due to their economic activity, tourism, and high levels of transience. Some of the most concerning areas include:
The South Figueroa Corridor, stretching from downtown LA to South Los Angeles, is known for its high prevalence of street-based sex trafficking. Victims, often minors and young adults, are coerced into prostitution and forced to work along this busy thoroughfare, where traffickers maintain strict control over their movements and earnings. Law enforcement crackdowns have led to temporary reductions in activity, but traffickers continue to exploit the area’s heavy foot traffic and anonymity.
Tourist-heavy areas such as Hollywood attract traffickers who seek to exploit the influx of visitors looking for illicit services. Many trafficking victims are brought to the area under the guise of modeling or acting opportunities, only to be forced into commercial sex work. Traffickers frequently use social media to recruit vulnerable individuals, offering them false promises of success in the entertainment industry.
LAX serves as a key transit point for traffickers moving victims in and out of the city. The airport’s vast network of domestic and international flights allows traffickers to transport individuals with minimal suspicion, often using forged documents or coercion to keep victims under control. Airport personnel and law enforcement have increased training efforts to identify trafficking signs and intervene before victims are moved across borders.
In the heart of downtown Los Angeles, the Garment District has been linked to numerous labor trafficking cases involving undocumented workers. Victims are often forced to work in sweatshops under exploitative conditions, with traffickers using threats of deportation to keep them silent. Efforts to regulate the industry and improve labor laws have had limited success, as traffickers continue to find ways to exploit loopholes in enforcement.
As one of the busiest ports in the United States, the Port of Los Angeles is a known entry and exit point for trafficking operations. Victims are often hidden within shipping containers or smuggled into the country under fraudulent employment contracts. Law enforcement efforts have focused on improving screening processes and collaborating with international agencies to identify and disrupt trafficking networks.
In response to the growing crisis, law enforcement agencies across Los Angeles have ramped up their efforts to identify and dismantle trafficking operations. The Los Angeles Police Department (LAPD) has created specialized task forces dedicated solely to human trafficking investigations. These units work in collaboration with federal agencies such as the FBI, Department of Homeland Security (DHS), and U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE).
The LAPD’s Human Trafficking Task Force, established in 2017, has conducted hundreds of sting operations targeting illicit massage parlors, brothels, and forced labor sites. These operations often involve undercover officers posing as potential clients to infiltrate trafficking networks and rescue victims. The task force also works closely with survivor advocacy groups to provide immediate support to those rescued, ensuring they receive medical care, legal assistance, and housing services.
In 2023, the LAPD reported that their joint operations resulted in over 200 arrests and the rescue of more than 150 victims. However, law enforcement officials acknowledge that arrests alone are not enough to solve the problem. Prosecuting traffickers presents significant challenges, as victims are often too traumatized or fearful to testify against their abusers, and traffickers use sophisticated legal loopholes to evade justice.
California’s legal framework has evolved to better address trafficking-related crimes. Proposition 35, passed in 2012, increased penalties for traffickers and mandated training for law enforcement officers on how to identify trafficking victims. Despite these measures, challenges remain, particularly when it comes to securing convictions. Defense attorneys frequently exploit gaps in victim testimonies, arguing that victims participated willingly, which further complicates prosecution efforts.
In addition to law enforcement, numerous advocacy groups have taken up the fight against trafficking in Los Angeles, offering direct services to victims and working to prevent future cases through education and outreach. Organizations such as CAST (Coalition to Abolish Slavery and Trafficking), Journey Out, and Saving Innocence provide holistic support, including trauma counseling, job training, and legal advocacy.
CAST, one of the leading anti-trafficking organizations in the city, has helped thousands of survivors reintegrate into society through their survivor leadership program, which empowers victims to become advocates within their own communities. They also work closely with businesses to educate employers about ethical hiring practices, ensuring they do not inadvertently support exploitative labor practices.
Survivor support networks play a crucial role in helping victims break free from the cycle of exploitation. Many survivors require long-term assistance, as the trauma associated with trafficking can take years to heal. Housing insecurity, legal challenges, and difficulties finding stable employment are just a few of the barriers survivors face after escaping their traffickers. Advocacy groups have called for increased funding to expand survivor services, emphasizing that addressing the root causes of vulnerability—such as poverty and lack of education—is essential in preventing trafficking from recurring.
Behind every statistic lies a deeply personal story of survival. Many trafficking survivors in Los Angeles recount harrowing experiences of coercion, abuse, and isolation. One survivor, Maria, was trafficked into the U.S. under the promise of a job in the hospitality industry but was instead forced into domestic servitude for years without pay. Maria’s story, like many others, highlights the deceptive tactics traffickers use to lure their victims.
Another survivor, Jasmine, shared her story of being recruited through social media at the age of 16. Lured by promises of modeling gigs, she was soon forced into commercial sex work, moving from hotel to hotel under the control of her trafficker. With the help of an outreach program, Jasmine was eventually able to escape and now works to educate others on the dangers of online recruitment tactics.
Survivors often face significant challenges in rebuilding their lives, as trauma, stigma, and legal hurdles can make reintegration difficult. Many rely on non-profit organizations such as CAST (Coalition to Abolish Slavery & Trafficking), Saving Innocence, and Journey Out, which provide housing, job training, and legal advocacy to help survivors regain independence.
Despite significant efforts, combating human trafficking in Los Angeles presents numerous challenges. One of the most pressing issues is the lack of public awareness. Many residents remain unaware of the signs of trafficking, which can occur in their neighborhoods, workplaces, and even within their social circles. Traffickers rely on this lack of awareness to operate under the radar, making it essential to educate the public on how to recognize red flags and report suspicions.
Another major challenge is the fragmented nature of trafficking networks. Traffickers frequently move victims across state and national borders to avoid detection, making it difficult for law enforcement to track and intervene in ongoing cases. This transient nature requires a high level of coordination between local, state, and federal agencies, which can often be hampered by bureaucratic inefficiencies.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has further exacerbated the trafficking crisis, with economic hardships increasing vulnerability among at-risk populations. Job losses, housing instability, and the shift to remote work have created new opportunities for traffickers to exploit individuals through online platforms. Reports indicate that traffickers have adapted their recruitment methods, using encrypted messaging apps and social media ads to lure potential victims under the guise of remote job opportunities.

Combating human trafficking requires a collective effort from law enforcement, policymakers, businesses, and the public. Raising awareness through education, supporting survivor-focused organizations, and reporting suspicious activities are essential steps that individuals can take to contribute to the fight against trafficking as it allows individuals to learn the red flags of human trafficking.
If you suspect human trafficking, you can report it through the National Human Trafficking Hotline at 1-888-373-7888 or contact local authorities. Signs of trafficking may include individuals showing signs of physical abuse, appearing fearful or disoriented, or being unable to speak freely about their circumstances.
By staying informed and engaged, Los Angeles residents can play a vital role in ensuring that their city becomes a safer place for everyone.
Human trafficking in Los Angeles is a complex and evolving crisis that demands ongoing attention and action. While law enforcement and advocacy groups have made significant strides, traffickers continue to exploit vulnerabilities within the city’s infrastructure. With increased public awareness, stronger policies, and continued collaboration, there is hope for a future where trafficking is eradicated, and victims can reclaim their lives.